***************************************************************************
Evaluation Criteria October:
40% Exam
20% Guide to exam
20% Speaking ability
10% Book and notebook
10% Classwork and participation
20% Guide to exam
20% Speaking ability
10% Book and notebook
10% Classwork and participation
***************************************************************************
Guías de Examen por Materia, Grado y Nivel
***************************************************************************
GUÍA DE EXAMEN SCIENCE HUMAN BODY, OCTUBRE 2016
Alumno: _________________________________________________
Grado: 1º _____, Sec: II, III, IV Intermediate
1.- Give names to the cell's structure:Grado: 1º _____, Sec: II, III, IV Intermediate
Chapter 1, section 1, Body Organization
A.- ______________________________
B.- ______________________________
C.- ______________________________
D.- ______________________________
2.- Give names to the four tissues:
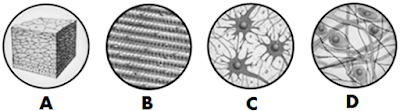
A.- ______________________________
B.- ______________________________
C.- ______________________________
D.- ______________________________
3-A Answer the questions:
1.- What's the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing? _____________
2.- What's the group of cells with similar structure? _________________________
3.- What tissue covers and protects underlying tissue? ______________________
4.- What tissue sends electrical signals through the body?____________________
5.- What tissue joints, supports, protects, nourishes and cushions organs?
_________________________________
6.- What's a group of tissues working together? ___________________________
7.- What's the group of organs wotrking together to perform a major function?
_________________________________
8.- How do we call the heart, the liver, the stomach, the kidneys or the lungs?
_________________________________
9.- What's the maintenance of a stable internal environment inside the body in a
changing external environment? _____________________________________
10.- Three examples are Cardiovascular, Muscular, and Skeletal. What are they?
___________________________________
3-B Match the organ systems with the names and main organ.
______ Muscular system - muscles
______ Endocrine systems - glandes
______ Skeletal system - bones
______ Circulatory system - heart
______ Nervous system - brain
______ Digestive system - intestines
______ Integumentary system - skin
Chapter 1, section 2, The skeletal system
4.- Give names to the bones in this skeleton:
5.- Answer the questions:
1.- What organ system has some functions like blood cell formation,
movement and protection? ________________________________________
2.- How many bones make up an average human adult skeleton? 206
3.- What's the place where two or more bones meet? A joint
4.- What are three examples of joints? _________________________________
________________________________________________________________
5.- What are strong elastic bands of connective tissue that hold joints together?
__________________________________
6.- What's a condition in which bones become less dense, weak and break
more easily? ___________________________________________________
7.- What's a painful disease in which joints may swell or stiffen? _____________
__________________________________
6.- Give names to the parts of the bone:
Chapter 1, section 3, The muscular system
7.- Answer the questions:
1.- What organ system has a primary functions movement and flexibility?
__________________________________________
2.- What are the three kinds of muscles? ________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
3.- What muscle is attached to your bones for movement? __________________
4.- What muscle moves food through the digestive system? _________________
5.- What muscle is found only in the heart? ______________________________
6.- What's the muscle movement that is under your control? _________________
7.- What's the muscle movement that is not under your control? ______________
8.- What are the strands of tough (hard) connective tissue that connect skeletal
muscle to the bones? _____________________________________________
9.- What exercise is a great way to strengthen skeletal muscles? _____________
10.- What exercise strengthens your heart and makes you more flexible? Some
examples are jogging, swimming, skating and cycling.____________________
11.- What's the injury in which a muscle or tendon is overstretched or torn?_____
____________________________________________
12.- What's the injury in which the tendons become inflamed? ________________
Chapter 1, section 4, The integumentary system
8.- Complete the definitions:
1.- The _______________________ system is made up of your skin, hair and nails.
2.- The two layers of the skin are the ________________________ and the
_________________________
3.- The ______________________ is the surface layer of skin in a plant or animal.
4.- The ______________________ is the layer of skin beneath (below) the epidermis.
5.- The chemical that determines skin color is the _______________________
6.- ____________________ is a protein that helps make the sking tough (hard);
it fills up dead epidermis cells.
7.- The dermis has many fibers made of a protein called ____________________
8.- Skin ____________________ is the injury when genetic material in cells is damaged
9.- ____________________ is the injury when too much oil clogs the hair follicles.
8.- Skin ____________________ is the injury when genetic material in cells is damaged
9.- ____________________ is the injury when too much oil clogs the hair follicles.
*************************************************************************
GUÍA DE EXAMEN USE OF ENGLISH, OCTUBRE 2016
Alumno: _________________________________________________
Grado: 1º _____, Sec: V, VI Advanced
Unit 1 All About You
1. Write antonyms to these adjectives
1. funny ____________________ 5. hard-working __________________
2. mean ____________________ 6. nice __________________________
3. strong ___________________ 7. polite _________________________
4. honest ___________________ 8. talkative _______________________
2. Match the activities with the pictures:
_____ They are talking and drinking. _____ He's playing golf
_____ They're dancing _____ He's hiking
_____ He's asking for directions _____ He's working in a lab
_____ They're having coffee _____ They're making a movie
_____ H'es traveling in a helicopter _____ H'es visiting Egypt
_____They're celebrating _____ He's taking an exam
_____ He's taking pictures _____ He's eating chicken
_____ He's playing videogames.
3.- Complete the sentences with present simple or continuous
1.- Joe usually ____________________(play) chess after school
2.- He ___________________________(not watch) tv
3.- What __________ his sister __________________(do) right now?
4.- She __________________________ (chat) online
5.- Why _______ she _______________(chat)?
6.- Because she __________(be) bored of the tv, too.
7.- How _______ they ____________(go) to school?
8.- They _______________(take) the bus.
9.- __________ you _______________(play) videogames?
10.- No, I ______________________(not use) the computer right now.
4.- Complete the sentences with gerund or infinitive form:
1.- Sarah always avoids ____________________(ask) her parents for money.
2.- My friends often decide ___________________(go) to Six Flags on Fridays.
3.- I'm always looking forward to __________________(make) new friends.
4.- She __________________________ (not pretend) to look smarter; she is!
5.- My parents can't stand ___________________(listen) to loud music.
6.- Why did Jane refused_________________(help) you?.
7.- I don't mind ____________ (work) on Saturdays if the pay is good.
8.- Who suggested ___________________(see) a film tonight? Fantastic!
9.- We hope _____________________(finish) school early today.
10.- I sometimes pretend ___________________ (be) a super star.
5.- Rewrite the sentences; add a modifying adverb.
1.- Sandy is ambitious and impatient. ( pretty / slightly)
_____________________________________________________________
2.- Matt isn't serious, but he's arrogant. (really / a bit)
_____________________________________________________________
3.- Melina is an honest person, and friendly. (quite / very)
_____________________________________________________________
4.- Nicole is confident, but impatient. (rather/ too)
_____________________________________________________________
5.- Johnny is smart, but a hard worker (not very / quite)
_____________________________________________________________
Unit 2 Winning and Losing
6.- Give names to these sports:
1. ________________________ 6. ________________________
2. ________________________ 7. ________________________
3. ________________________ 8. ________________________
4. ________________________ 9. ________________________
5. ________________________ 10. _______________________
7.- What sports are used with play, go or do? Complete the list:
Play Go Do
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
___________________ ___________________ ___________________
8.- Complete the sentences with past simple and auxiliary did / didn't
1.- What __________ you_____________(do) last weekend?
2.- We _______________(go) to the museum.
3.- __________ you __________________(have) a good time?
4.- Yes, we __________________(see) some interesting paintings.
5.- Great! When ____________ you ____________(visit) the museum?
6.- On Saturday, and on Sunday we ________________(play) soccer in the park.
7.- _________ you _____________(win) the game?
8.- No, but we ______________(have) a lot of fun!
9.- Complete the sentences with past simple and continuous:
1.- When I __arrived _(arrive) at Sam's party, lots of people
__were dancing __________(dance) in the living room.
2.- I ___got_______ (get) into the kitchen and __saw____(see)
that Mike ____was____ (be) there.
3.- He ___was standing_________(stand) in front of the refrigerator and
___was eating_____________(eat) some pizza.
4.- I ____said________(say) Hello, but he ___didn't hear_________
(not hear) me.
5.- I ___left_____(leave) the kitchen and ___went_______(go)
into the living room.
6.- Linda ____was sitting______(sit) on the stairs.
7.- She ___was holding_______(hold) her head in her hands; her shoulders
______were shaking______(shake), but she ____wasn't crying_
(not cry); she _______was laughing_________(laugh).
10.- Complete the sentences with past simple and auxiliary did / didn't
1.- What __________ you_____________(do) last weekend?
2.- We _______________(go) to the museum.
3.- __________ you __________________(have) a good time?
4.- Yes, we __________________(see) some interesting paintings.
5.- Great! When ____________ you ____________(visit) the museum?
6.- On Saturday, and on Sunday we ________________(play) soccer in the park.
7.- _________ you _____________(win) the game?
8.- No, we _________. But we ______________(have) a lot of fun!
***************************************************************************
GUÍA DE EXAMEN SCIENCE ENVIRONMENTAL, OCTUBRE 2016
Alumno: _________________________________________________
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: II, III, IV Intermediate
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: II, III, IV Intermediate
Chapter 1, section 1, Everything is Connected
1.- Give names to the diagram parts. (see picture in the book, page 6)
1.- Give names to the diagram parts. (see picture in the book, page 6)
4.- ___________________________________
3.- ___________________________________
2.- ___________________________________
1.- ___________________________________
2.- Complete the definitions:
1.- A single living thing like a prairie dog is called an ________________________
2.- All the living parts of the environment such as plants and animals make up the
____________________ factors in the environments
3.- All the nonliving parts of the environment such as water. soil, temperature and
light make up the ____________________ factors in the environment.
4.- A _________________________ is made of a group of similar organisms.
5.- A _________________________ is formed by different groups of populations.
6.- A community of organisms living in their abiotic environment make up an
______________________________________
7.- The _______________________ is the place of Earth where life exists.
8.- ______________________ is the study of the interaction of living organisms
with one another and with their environment.
Chapter 1, section 2, Living things need Energy
3.- Answer the questions:
1.- What's the source of energy for almost all living things?
___________________
2.- What are the organisms that use sunlight to make food?
___________________
3.- What are the organisms that eat other organisms?
________________________
4.- What are the organisms that eat only aminals?
___________________________
5.- What are the organisms that eat only plants?
____________________________
6.- What are the organisms that eat both plants and animals?
______________________________
7.- What kind of herbivore eats dead plants and animals?
_______________________
_______________________
8.- What organisms get energy by breaking down dead organisms?
______________________________
9.- What kind of organisms are bacteria and fungi?
__________________________
10.- What is a diagram that shows the feeding relationships between organisms?
______________________________
11.- What is a diagram that shows how energy in food flows from one organism
to another?
_____________________________________________________
12.- What is a triangular diagram that shows an ecosystem loss of energy?
______________________________
4.- Choose the best answer, write the letter on the line.
Detritus: solid
decomposed remains
from animals and
plants
1. _____ What is the correct food chain of four organisms?
A) Cord grass B) Detritus C) Cord grass
Periwinkle snail grass shrimp detritus
Blue crab blue crab diamondblack terrapin
Herring gull sheepshead minnow otter
2. _____ What is the correct food chain including a producer?
A) Cord grass B) Cord grass C) Grass shrimp
Blue crab periwinkle snail sheepshead minnow
Herring gull blue crab otter
3. _____What is a correct food chain with no producer?
A) Cord grass B) Periwinkle snail C) Cord grass
Periwinkle snail diamondblack terrapin grass shrimp
Sheepshead minnow herring gull blue crab
Herring gull
4. _____What is a correct food chain of three organisms?
A) Cord grass B) Detritus C) Grass shrimp
Periwinkle snail diamondblack terrapin Sheepshead minnow
Sheepshead minnow blue crab otter
5.- Answer the questions:
1.- What are the resources that are so scarce that limit the size of a population?
__________________________________________
2.- What is the largest population that an environment can support?
__________________________________________
3.- What are the three types of Interaction between organisms?
________________________________________________________________
6.- Complete the sentences.
1. __________________________ is when two or more individuals or populations
try to use the same resources to live
2. __________________________ is the organism that hunts, kills and eats parts
or all of another organism.
3. __________________________ is the organism that is killed and eaten.
4. ________________________________ is the group of methods and abilities
of organisms to keep from being eaten.
5.__________________________ is a relationship in which two organisms live
in close association with each other.
6. __________________________ is a relationship between two species in which
both species benefit.
7. __________________________ is a relationship in which one organism
benefits and the other is unaffected.
7. __________________________ is a relationship in which one organism
benefits and the other is unaffected.
8. __________________________ is a symbiotic relationship in which
one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
9. _______________________ is the organism that benefits from the host, one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
harming it.
10. Pollinator is an organism that carries pollen from
one flower to another.
11. __________________________ is a long term evolution of two species
because of their close interaction.
because of their close interaction.
7. Explain and provide examples of the next concepts:
1. Camouflage: _________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
2.- Defensive chemicals: __________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
3. Warning coloring: ______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
*************************************************************************
GUÍA DE EXAMEN LITERATURE, OCTUBRE 2016
Alumno: _________________________________________________
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: V, VI, VII Advanced
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: V, VI, VII Advanced
Bonne
Anéé (collection 1, page 31)
I. Answer the questions.
1. What are the two locations of this essay?
_____________________________
2. Who are these persons?
a) The writer and narrator. _________________________________________
b) Ruthless dictator François
Duvalier. _______________________________
c) Jean Claude Duvalier. __________________________________________
3. What does “Bonne Anée” mean? ___________________________________
4. When and where do the essay events start? __________________________
5. What are the men discussing? _____________________________________
6. Where are the women? ___________________________________________
7. What happens with the kids? ______________________________________
8. What language predominates in the men’s discussion? __________________
9. What languages does the narrator understand? ________________________
10. What’s the topic of discussion? ____________________________________
11. What does he remember from Haiti? ________________________________
12. When does he understand Papa Doc is an evil man? ___________________
13. What are the predictions for the dictator’s death? ______________________
14. When do the exiles celebrate Papa Doc’s disappearance? _______________
15. How long was he in power? _______________________________________
16. How did he die? ________________________________________________
17. Who gets the power after him? ____________________________________
18. How long does he stay in power? __________________________________
19. When does Haiti participate in a World Cup for the first time? _____________
20. How long does Haitian victory last against Italy? _______________________
21. When does BéBé Doc flee
the country? ______________________________
22. When does Jean Pierre Benoit (the narrator) go to Haiti for two
weeks? _____
_____________________________________________________________
Frederic
Douglas (collection 3, page 143)
II. This summary is mixed. Put the events in order.
_____ Frederick Douglas lived in
Master Hugh’s family for seven years.
_____ He gave bread to poor
children in exchange for knowledge.
_____ Mistress Hugh changed her
attitude and her tender heart became stone.
_____ He understood how his race
became slaves; he started to abhor and detest
his enslavers.
_____ His mistress taught him to
read; he describes her as a kind and
tender-hearted woman.
tender-hearted woman.
_____ He got a book entitled “The
Columbian Orator”. By reading it, he discovers
the concept of emancipation as freedom.
the concept of emancipation as freedom.
_____ In that book, he also reads
Sheridan’s speeches about freedom and
human rights.
human rights.
_____ He says she treated him as
a human being, not a chattel, who he was.
_____ After knowing this, he
starts to see his ability to read as a curse, not
a blessing.
a blessing.
_____ He adopted a plan to keep
learning. He meets white boys on the street and
turn them into
teachers.
_____ He is twelve when he gets
aware of his condition as slave; his heart suffers.
_____ She stops instructing him
and gets more violent than her husband against
his learning.
_____ He is put into surveillance
for not having any reading material with him.
_____ In the end, there is only
an idea: Freedom. It’s inserted deeply in his mind
and will never leave.
and will never leave.
Harriet Tubman (collection 3, page 151)
III. Answer the questions.
1. Who was Ann Petry? ___________________________________________
2. Who was one of the most famous “conductors” of the Underground
Railroad?
____________________________________________________________
3. When did the events take place? __________________________________
4. There was an unknown man that was running off slaves. How was he
named?
____________________________________________________________
5. Who was him, actually? _________________________________________
6. When did she take the fugitive slaves in a dangerous journey to
Canada?
____________________________________________________________
7. What was the season? __________________________________________
8. How did she announce that she was there, outside the quarter?
____________________________________________________________
9. What was the song line she used to sing? ___________________________
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
10. What did the slaves say when they heard that song?
__________________
11. Now, you get why she was the mysterious man? _____________________
12. How many parties ran away that time? _____________________________
13. When had she been in Canada before that journey? __________________
14. When did they used to sleep and walk? ____________________________
____________________________________________________________
15. They were slaves, somebody’s property. How much were they valued?
____________________________________________________________
16. Where did they make their first stop? ______________________________
17. When she knocked at the door and the man responded “who is it?”, she
gave
a secret password. What did
she say? ____________________________
18. When she wasn’t welcomed, they all got desperate. What did she do
and why?
____________________________________________________________
19. Where was their second stop? ___________________________________
20. How was the journey, especially when they left the warmth of the
German’s
house?_____________________________________________________
house?_____________________________________________________
21. What happened when a slave claimed, “Let me go back”? _____________
____________________________________________________________
22. Where did they stop next? ______________________________________
23. Where did they reach after some more stops? _______________________
24. Who had a record of the runaway slaves and published, in 1872, a
book called
“The Underground Railroad”?
____________________________________
25. Who received them when they got to Rochester? ____________________
26. When did they reach Canada? ___________________________________
27. So, finally, what was the famous Underground Railroad?
______________
____________________________________________________________
VOCABULARY
IV. Match the words with the definitions
Abbreviations: (n) noun
/ (v) verb
/ (adj) adjective
/ (adv) adverb
Bonne
Anéé (collection 1, page 31)
1. to predominate (v) ____
to deprive someone from his / her
possessions
possessions
2. a military coup (n) ____ to run away, to escape from
danger
3. to dawn (v) ____
abandoned, left behind
4. dispossessed (adj) ____
to start an event
5. unmistakable (adj) ____
more common
6. to flee (v) ____
clear, evident
7. forsaken (adj) ____
a government taken by force
8. natal (adj) ____ referred to birth
Frederic
Douglas (collection 3, page 143)
1. to commence (v) ____
common sense
2. a chattel (n) ____ a slave
3. narrowly (adv) ____
closely
4. errands (n) ____ to start, begin
5. prudence (n) ____ miserable
6. to bear (v) ____
tasks
7. denunciation (n) ____
to endure
8. to abhor (v) ____ public condemnation
9. wretched (adj) ____ to hate
Harriet Tubman (collection 3, page 151)
1. goodly (adj)
____ to walk erratically, as if one were dizzy
2. hastily (adv) ____ looking
messy and dirty, as homeless
3. party (n) ____
to make someone remember things from the past
4. to dishevel (v) ____
considerable, important in number
5. to instill (v) ____
a group of individuals
6. to stumble (v) ____
precipitated, in a hurry manner
7. to linger (v) ____
to introduce or supply gradually
8. to evoke (v) ____ to remain or stay longer
*************************************************************************
GUÍA DE EXAMEN SCIENCE ENVIRONMENTAL, OCTUBRE 2016
Alumno: _________________________________________________
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: V, VI, VII Advanced
Grado: 2º _____, Sec: V, VI, VII Advanced
Chapter 1, section 1, Everything is Connected
1.- Give names to the Levels of Organization:
(see picture in the book, page 6)
1.- Give names to the Levels of Organization:
(see picture in the book, page 6)
5.- ___________________________________
4.- ___________________________________
3.- ___________________________________
2.- ___________________________________
1.- ___________________________________
2.- Complete the definitions:
1.- A single living thing like a prairie dog is called an ________________________
2.- All the living parts of the environment such as plants and animals make up the
____________________ factors in the environments
3.- All the nonliving parts of the environment such as water. soil, temperature and
light make up the ____________________ factors in the environment.
4.- A _________________________ is made of a group of similar organisms.
5.- A _________________________ is formed by different groups of populations.
6.- A community of organisms living in their abiotic environment make up an
______________________________________
7.- The _______________________ is the place of Earth where life exists.
8.- ______________________ is the study of the interaction of living organisms
with one another and with their environment.
Chapter 1, section 2, Living things need Energy
3.- Answer the questions:
1.- What's the source of energy for almost all living things?
___________________
2.- What are the organisms that use sunlight to make food?
___________________
3.- What are the organisms that eat other organisms?
________________________
4.- What are the organisms that eat only animals?
___________________________
5.- What are the organisms that eat only plants?
____________________________
6.- What are the organisms that eat both plants and aminals?
______________________________
7.- What kind of herbivore eats dead plants and animals?
_______________________
_______________________
8.- What organisms get energy by breaking down dead organisms?
______________________________
9.- What kind of organisms are bacteria and fungi?
__________________________
10.- What is a diagram that shows the feeding relationships between organisms?
______________________________
11.- What is a diagram that shows how energy in food flows from one organism
to another?
_____________________________________________________
12.- What is a triangular diagram that shows an ecosystem loss of energy?
______________________________
4.- Choose the best answer, write the letter on the line.
Detritus: solid
decomposed remains
from animals and
plants
5.- Answer the questions:
1.- What are the resources that are so scarce that limit the size of a population?
__________________________________________
2.- What is the largest population that an environment can support?
__________________________________________
3.- What are the three types of Interaction between organisms?
________________________________________________________________
6.- Complete the sentences.
harming it.
10. Pollinator is an organism that carries pollen from
one flower to another.
7. Provide three examples of the next organisms.
8. Explain and provide examples of the next concepts:
1. Camouflage: _________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
2.- Defensive chemicals: __________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
3. Warning coloring: ______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
__________________________
10.- What is a diagram that shows the feeding relationships between organisms?
______________________________
11.- What is a diagram that shows how energy in food flows from one organism
to another?
_____________________________________________________
12.- What is a triangular diagram that shows an ecosystem loss of energy?
______________________________
4.- Choose the best answer, write the letter on the line.
Detritus: solid
decomposed remains
from animals and
plants
1. _____ What is the correct food chain of four organisms?
A) Cord grass B) Detritus C) Cord grass
Periwinkle snail grass shrimp detritus
Blue crab blue crab diamondblack terrapin
Herring gull sheepshead minnow otter
2. _____ What is the correct food chain including a producer?
A) Cord grass B) Cord grass C) Grass shrimp
Blue crab periwinkle snail sheepshead minnow
Herring gull blue crab otter
3. _____What is a correct food chain with no producer?
A) Cord grass B) Periwinkle snail C) Cord grass
Periwinkle snail diamondblack terrapin grass shrimp
Sheepshead minnow herring gull blue crab
Herring gull
4. _____What is a correct food chain of three organisms?
A) Cord grass B) Detritus C) Grass shrimp
Periwinkle snail diamondblack terrapin Sheepshead minnow
Sheepshead minnow blue crab otter
5.- Answer the questions:
1.- What are the resources that are so scarce that limit the size of a population?
__________________________________________
2.- What is the largest population that an environment can support?
__________________________________________
3.- What are the three types of Interaction between organisms?
________________________________________________________________
6.- Complete the sentences.
1. __________________________ is when two or more individuals or populations
try to use the same resources to live
2. __________________________ is the organism that hunts, kills and eats parts
or all of another organism.
3. __________________________ is the organism that killed and eaten.
4. ________________________________ is the group of methods and abilities
of organisms to keep from being eaten.
5.__________________________ is a relationship in which two organisms live
in close association with each other.
6. __________________________ is a relationship between two species in which
both species benefit.
7. __________________________ is a relationship in which one organism
benefits and the other is unaffected.
7. __________________________ is a relationship in which one organism
benefits and the other is unaffected.
8. __________________________ is a symbiotic relationship in which
one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
9. _______________________ is the organism that benefits from the host,one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
harming it.
10. Pollinator is an organism that carries pollen from
one flower to another.
11. __________________________ is a long term evolution of two species
because of their close interaction.
because of their close interaction.
7. Provide three examples of the next organisms.
1.- Scavenger: Vulture turkey, hyenas and crows
2.- Decomposer: Worms, ________________ and _______________________
3.- Producers: __________________, algae and seaweed
4.- Carnivore: ____________________________________________________
5.- Herbivore: ____________________________________________________
6.- Omnivore: ____________________________________________________
8. Explain and provide examples of the next concepts:
1. Camouflage: _________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
2.- Defensive chemicals: __________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
3. Warning coloring: ______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
examples:______________________________________________________
9. Match questions and answers.
1. What happens if the rainy season in an ecosystem is less than the one last year?
_____
2. What happens if, in a habitat, plants cannot get enough sunlight? _____
3. What happens if climate conditions change in an ecosystem? _____
4. What happens if the food is not enough for a certain population? _____
4. What happens if the food is not enough for a certain population? _____
5. Wolves’ diet includes eating rabbits. What happens if wolves disappear? _____
6. How does a limiting factor work in an ecosystem? ______
6. How does a limiting factor work in an ecosystem? ______
A. The population of rabbits increases.
B. The growth of many plants and trees will be reduced, competition will be harder.
C. Species and Populations emigrate to a better place or adapt to survive.
D. They cannot produce food, there’s no photosynthesis.
E. The population will start fighting for it; only the strongest will survive.
F. The limited resource will make the weakest population die and the balance
of the carrying capacity be restored.
*************************************************************************E. The population will start fighting for it; only the strongest will survive.
F. The limited resource will make the weakest population die and the balance
of the carrying capacity be restored.















